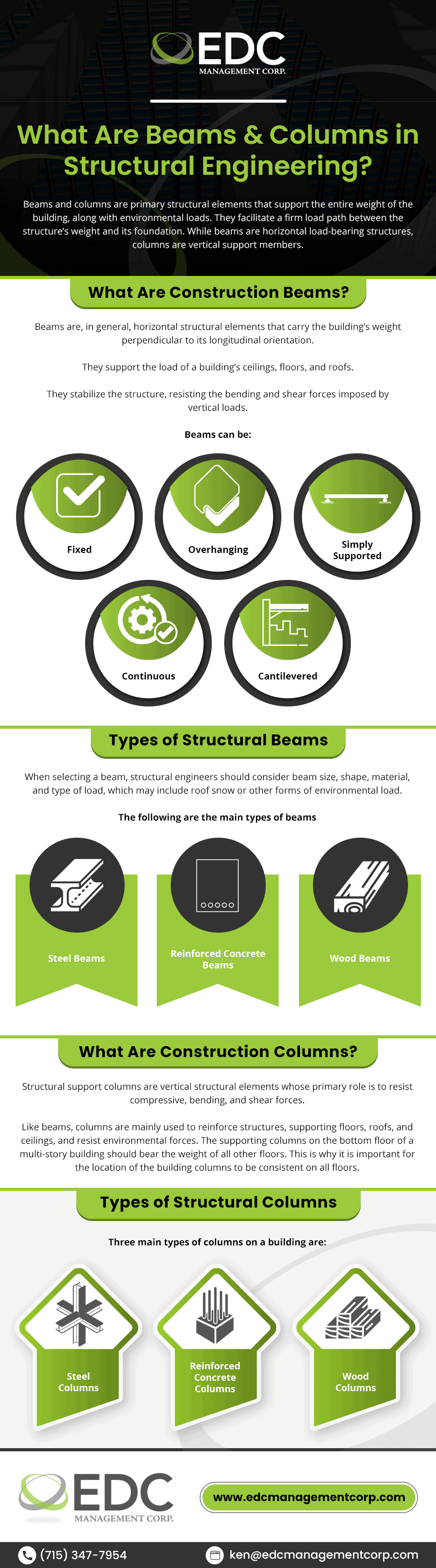
What Are Building & Equipment Foundations?
1 CommentNecessary for all load-bearing structures, the foundation of a building or a piece of equipment is critical for providing support and helping distribute load. Foundations allow the soil around them to take the pressure of a structure’s weight, rather than the building or equipment itself. An even load distribution plays an important role in stabilizing final structures and managing settlement since the ground below buildings naturally shifts over time.
Understanding the importance of foundation work in construction and the different factors involved in structural integrity can ensure that engineers select the correct structure foundation type and size when beginning a new project to safeguard against foundation system failure and, in turn, structural collapse.
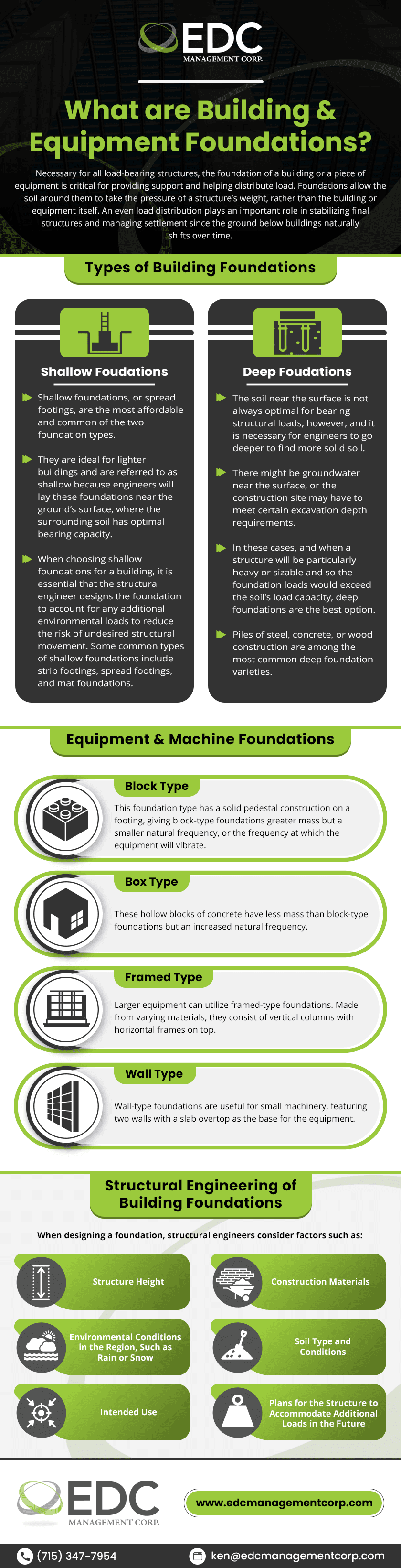
Types of Building Foundations
There are two building foundation types: shallow and deep. When choosing the best foundation type for a construction project, the common considerations include soil type and current and future building loads.
Shallow Foundations
Shallow foundations, or spread footings, are the most affordable and common of the two foundation types. They are ideal for lighter buildings and are referred to as shallow because engineers will lay these foundations near the ground’s surface, where the surrounding soil has optimal bearing capacity. When choosing shallow foundations for a building, it is essential that the structural engineer designs the foundation to account for any additional environmental loads to reduce the risk of undesired structural movement. Some common types of shallow foundations include strip footings, spread footings, and mat foundations.
Deep Foundations
The soil near the surface is not always optimal for bearing structural loads, however, and it is necessary for engineers to go deeper to find more solid soil. There might be groundwater near the surface, or the construction site may have to meet certain excavation depth requirements. In these cases, and when a structure will be particularly heavy or sizable and so the foundation loads would exceed the soil’s load capacity, deep foundations are the best option. Piles of steel, concrete, or wood construction are among the most common deep foundation varieties.
Equipment & Machine Foundations
While foundations are necessary for constructing buildings, they are also important for heavy equipment and machinery. The design of the equipment’s foundation should allow it to withstand the shocks and vibrations of the supported machine or tool. Four types of equipment foundations are:
- Block type. This foundation type has a solid pedestal construction on a footing, giving block-type foundations greater mass but a smaller natural frequency, or the frequency at which the equipment will vibrate.
- Box type. These hollow blocks of concrete have less mass than block-type foundations but an increased natural frequency.
- Framed type. Larger equipment can utilize framed-type foundations. Made from varying materials, they consist of vertical columns with horizontal frames on top.
- Wall type. Wall-type foundations are useful for small machinery, featuring two walls with a slab overtop as the base for the equipment.
Structural Engineering of Building Foundations
The integrity of structures depends on quality structural engineering before and during construction. As part of a subsection of civil engineering, structural engineers analyze gravitational and other forces that will act on a structure, material usage, and all of the load-bearing requirements of a project. These engineers will make precise calculations as well as structural drawings to carefully plan the load distribution and help construct safe, sturdy buildings that will be structurally sound.
In addition to the load weight of the structure or equipment, structural engineers prepare the foundation for other loads that may impact structural integrity to determine the ideal foundation size and type for the project. When designing a foundation, structural engineers consider factors such as:
- Structure height
- Construction materials
- Environmental conditions in the region, such as rain or snow
- Soil type and conditions
- Intended use
- Plans for the structure to accommodate additional loads in the future
Engineering, Design, & Construction Management Services From EDC Management Corp.
Structural engineering helps achieve sound foundations for safe, strong buildings and equipment. At EDC, we provide clients with a wide range of structural and mechanical engineering and design services, along with construction site management. We’ve been providing successful solutions to the commercial, industrial, and architectural sectors since 2013, and our knowledgeable team offers over 130 years of combined experience in engineering and design. Contact us to learn more about our services, or request a quote today to begin your project with EDC.